Broad Peaks
GC Troubleshooting Course
6 - Unstable Baseline
7 - Carryover/Ghost Peaks
8 - Fronting Peaks
9 - Poor Peak Resolution
10 - Split Peaks
11 - Response Variability
12 - Retention Time Variability
13 - Course Summary & Test
Broad Peaks
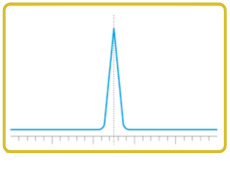
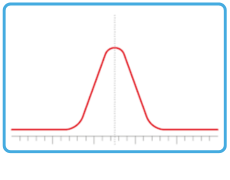
Broad peaks reduce resolution, make quantification less reliable, and may be a sign of poor system performance or suboptimal method settings. If your chromatogram shows broader-than-expected peaks, follow a structured diagnostic approach.
Step 1: Rule out system faults
Start with basic hardware and setup checks:
1. Check for dead volume: Dead volume refers to unwanted empty space in the carrier gas flow path, which causes band broadening.
Actions:
- Ensure the column is installed correctly and at the proper depth.
- Avoid using oversized or mismatched fittings, connectors, or ferrules.
- Use properly fitted inlet liners with no unnecessary voids.
2. Check carrier gas flow: Low carrier gas flow can slow analyte movement, causing dispersion and broadening.
Actions:
- Verify flow settings in the software and instrument.
- Adjust linear velocity to match column specifications.
- Check for flow controller faults or restrictions in the lines.
Step 2: Evaluate method parameters
If the system looks good, investigate the method:
1. Check for Outdated or Modified Methods
- Has the method been transferred from another instrument without optimisation?
- Has someone tweaked parameters (e.g., temperature ramps, hold times) without documentation?
Action: Compare current method settings to validated or original SOPs.
2. Column Suitability
- Is the film thickness or column length appropriate for the analyte volatility and load?
- A thick film or long column can increase analyte retention and peak broadening.
Action: Try using a shorter column or one with a thinner stationary phase film.
3. Oven Temperature Program
- A slow ramp or low start temp can cause wide peaks, especially for early eluters.
Actions:
- Increase the temperature ramp rate.
- Consider reducing the initial oven temperature hold time.
- Optimise ramping for sharper elution.
Tip: Use online chromatogram modelling tools to simulate the effect of different columns, carrier gases, and ramp rates on resolution and peak shape.
Comparison of chromatograms before and after a change of method
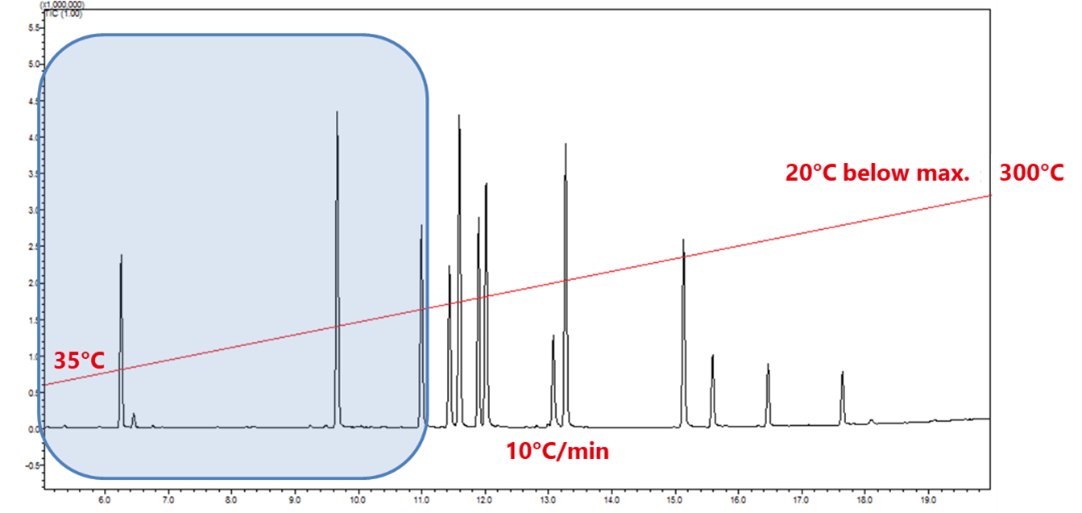
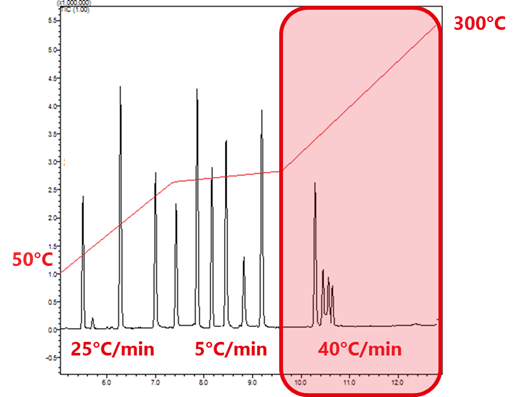
A tweak to the method is often sufficient to resolve problems with broad peaks
– as exemplified in this case where the method was optimised to reduce runtime from 20 minutes to under 13 minutes with optimum separation for desired compounds.
If none of those things solve the problem, then consider whether the problem could be down to carryover (we’ll cover that in detail in our Week 4 module).
Broad Peaks Troubleshooting Summary
| Category | Check | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware |
- Dead volume (connectors, liner, column fit) - Low carrier gas flow |
- Reinstall or replace faulty parts - Increase flow rate or check controller |
| Method |
- Unsuitable method transfer or edits - Thick film or long column - Poor oven program |
- Re-optimise or revert to original SOP - Use thinner/shorter column - Raise ramp rate, reduce hold times |
| Advanced |
- Carryover or degradation |
- Check sample prep and injection protocol |
Related Resources